THz spectroscopy
The only commercial device capable of performing terahertz spectroscopy of aqueous solutions
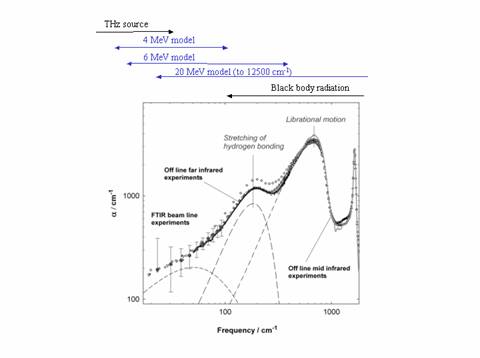
Mid-infrared (MIR) light, which has traditionally been used as the fingerprint region for molecular spectroscopy, corresponds to intramolecular vibrations. Within far-infrared (FIR) light, the electromagnetic radiations with a wavelength between 100 μm and 1 mm are called “terahertz light” and correspond to weak interactions such as intermolecular vibrations and hydrogen bonds. Therefore, this light can be used to obtain information on the network structure of polar solvents such as water. Terahertz light is also suited for observing the lattice structure of crystals.
The radiant power of our terahertz spectroscopy device using MIRRORCLE-6FIR as the light source surpasses that of a large-scale synchrotron radiation.
Analysis example : absorption spectrum of water
Analysis example : absorption spectrum of an acetone water mixture
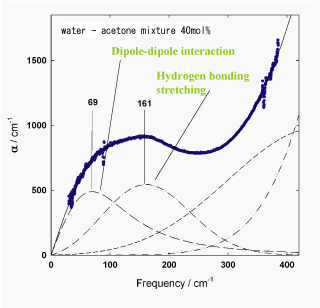
The graph reflects the presence of hydrogen bonding in water as well as the dipole interaction of acetone.
| Light source | MIRRORCLE-6FIR |
|
Measurement wavelength range |
1cm or above (wavelength of 1 mm or less) |
|
Spectrometer
|
Fourier transform infrared spectrometer |
| detector | Silicone borometer |
|
Sample format
|
Solid, liquid, etc. (please contact us) |
| Resolution | 0.25cm-1 |
